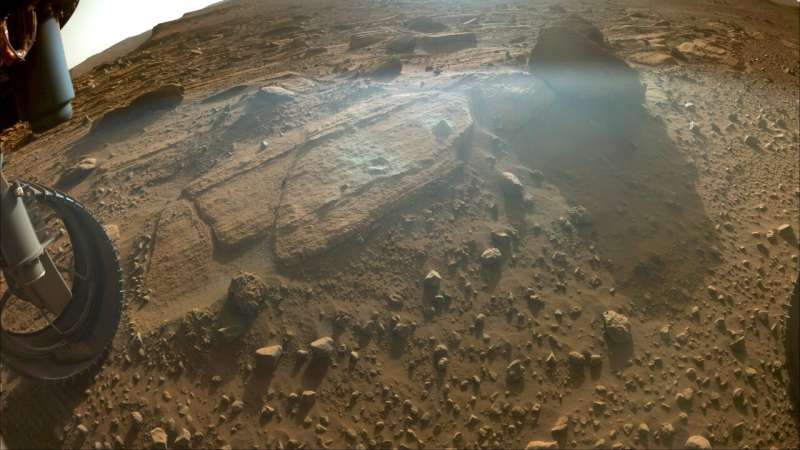
This image reveals the rocky outcrop the Perseverance science group calls Berea after the NASA Mars rover drawn out a rock core and abraded a circular spot. The image was taken by the rover’s Mastcam-Z instrument on March 30, 2023. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/ MSSS
NASA’s Perseverance rover cored and saved the very first sample of the objective’s most recent science project on Thursday, March 30. With each project, the group checks out and studies a brand-new location. On this one, the rover is checking out the top of Jezero Crater’s delta. Determination has actually gathered an overall of 19 samples and 3 witness tubes, and it just recently transferred 10 tubes as a backup cache on the Martian surface area as part of the NASA-ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Sample Return project.
Researchers wish to study Martian samples with effective laboratory devices in the world to look for indications of ancient microbial life and to much better comprehend the water cycle that has actually formed the surface area and interior of Mars.
Cored from a rock the science group calls “Berea,” this newest sample is the 16th cored rock sample of the objective (there are likewise samples of regolith– or damaged rock and dust– along with Mars environment; learn more about the samples). The science group thinks Berea formed from rock deposits that were brought downstream by an ancient river to this area. That would imply the product might have originated from a location well beyond the boundaries of Jezero Crater, and it’s one reason the group discovers the rock so appealing.
“The 2nd factor is that the rock is abundant in carbonate,” stated Katie Stack Morgan, deputy job researcher for Perseverance at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “Carbonate rocks in the world can be proficient at protecting fossilized lifeforms. If biosignatures existed in this part of Jezero Crater, it might be a rock like this one that might effectively hold their tricks.”
A Climate Puzzle
One huge puzzle is how Mars’ environment worked back when this location was covered with liquid water. Since carbonates form due to chemical interactions in liquid water, they can supply researchers a long-lasting record of modifications in the world’s environment. By studying the carbonate in the Berea sample, the science group might assist fill out the spaces.
“The Berea core highlights the appeal of rover objectives,” stated Perseverance’s task researcher, Ken Farley of Caltech in Pasadena. “Perseverance’s movement has actually enabled us to gather igneous samples from the reasonably flat crater flooring throughout the very first project, and after that take a trip to the base of the crater’s delta, where we discovered fine-grained sedimentary rocks transferred in a dried lakebed. Now we are tasting from a geologic place where we discover grainy sedimentary rocks transferred in a river. With this variety of environments to observe and gather from, we are positive that these samples will permit us to much better comprehend what happened here at Jezero Crater billions of years earlier.”
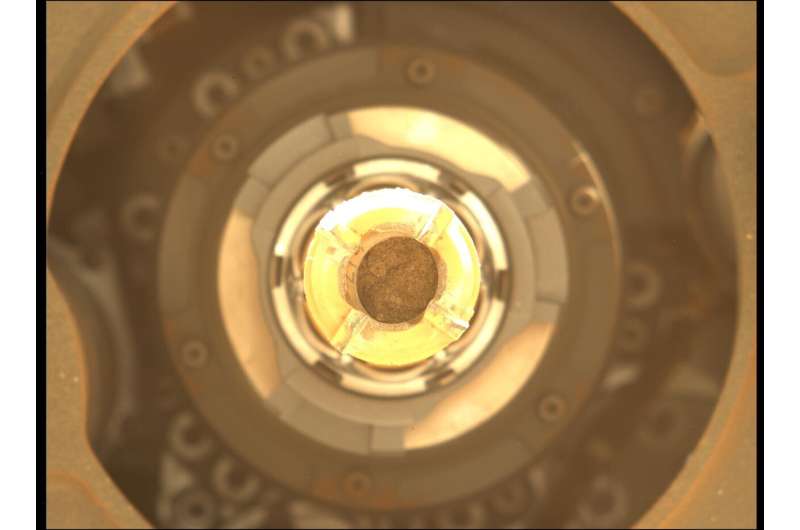

This image reveals the rock core from Berea inside the drill of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover. Each core the rover takes has to do with the size of a piece of class chalk: 0.5 inches (13 millimeters) in size and 2.4 inches (60 millimeters) long. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/ MSSS
With this most current sample saved securely in a sample tube in the rover’s stomach, the six-wheeler will continue to climb up Jezero’s sedimentary fan towards the next bend in the dry riverbed, a place the science group is calling “Castell Henllys.”
Citation: Perseverance rover gathers very first Mars sample of brand-new science project (2023, April 1) recovered 1 April 2023 from https://phys.org/news/2023-04-perseverance-rover-mars-sample-science.html
This file undergoes copyright. Apart from any reasonable dealing for the function of personal research study or research study, no part might be recreated without the composed consent. The material is attended to details functions just.