A revolutionary strategy established by scientists connected with the USC Michelson Center for Convergent Bioscience provides a brand-new method of event and arranging extremely detailed details about natural tissues in record time.
The approaches might at some point be utilized to quickly process tissue biopsies in cancer care or spotting germs in food processing plants.
Tissues release signals, or intrinsic fields, that while noticeable are really weak and difficult to separate. The method, detailed in a set of documents released in Nature Methodsand Cell Reports Methods utilizes an intricate mathematical algorithm to enhance the quality of the signals and after that separate them.
The brand-new method is similar to how a streaming service provides various levels of compression to guarantee their video corresponds despite a user’s web connection, according to Francesco Cutrale, co-principal detective and research study assistant teacher at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering.
“Based on how quick your connection is, the banner will send out the video with various levels of compression that is then recomposed efficiently for your gadget,” he stated. “We’re doing something comparable: We’re taking huge, extremely intricate information and moving it into an area where it is compressed. We can then take a look at huge information sets– associated by resemblance into a huge pie chart– and examine this information in record time and with extremely high level of sensitivity.”
A window into the intricacy of cells and natural tissue
The algorithm– detailed in Nature Methodspreviously this year– continues the current improvement of high-content imaging techniques making use of fluorescence. Thanks to its high contrast and uniqueness, along with its flexibility, fluorescence has actually allowed the detection and specifying of particular particles. These more recent methods do not work for imaging live, or in vivo, samples since these methods have actually restricted level of sensitivity and might harm specimens.
In the paper, the research study group demonstrated how the method, called Hybrid Unmixing, might be utilized to evaluate live natural tissue easily and effectively. The strategy utilizes direct unmixing, an approach to evaluate various parts within a specimen marked by chemical substances called fluorophores.
They then envision these parts utilizing hyperspectral phasors, which utilize the whole color spectrum, instead of exclusively red, blue and green. In doing so, Hybrid Unmixing enables synchronised imaging of intense and dim identified elements within natural tissue, even under low lighting.
Enabling concurrent analysis of the cellular habits and cellular metabolic process of these identified parts, the method will offer more precise insights into the intricacy of biological systems.
“There’s a push in the research study area for comprehending intricate biological systems,” Cutrale stated.
“While scientists usually take a look at just 2 or 3 labels at the same time, the reality is that there are more than simply a couple of aspects connecting within cells. The obstacle is that these signals typically appear really comparable, making them hard to differentiate. In our paper, we have actually effectively determined and separated approximately 14 various signals. This advancement will supply scientists with a more detailed understanding of the activity inside cellular and biological systems.”
The algorithm supplies the structure for many applications from a market perspective, Cutrale stated.
“We operate in the life sciences, however it’s simple to think of various applications to assess the quality of fruits, the existence of pesticides or how to enhance production in numerous other fields,” he stated.
SHy-Cam deals low-priced, top quality imaging tool
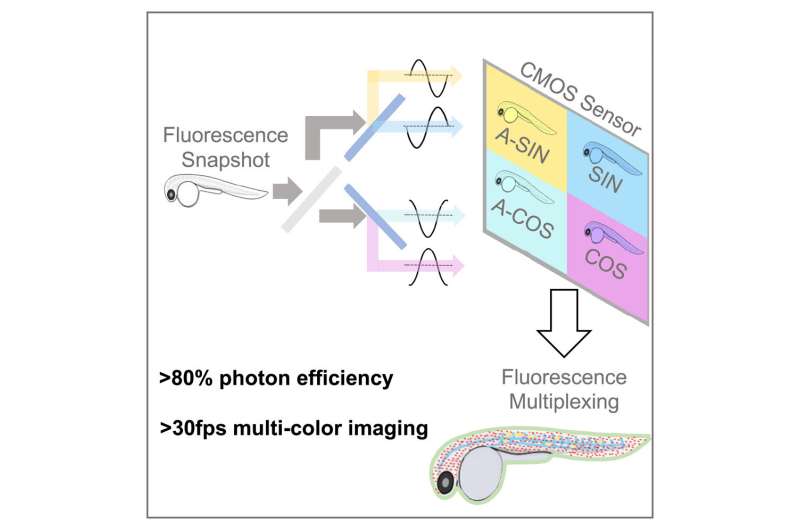
A subsequent paper, released today in Cell Reports Methods explains hardware– called SHy-Cam, brief for Single-shot Hyperspectral Phasor Camera– developed by the research study group enhanced to catch this kind of info. Normal tissue-imaging methods using fluorescence usage color channels throughout the spectrum to make up for overlap in between labels. This method decreases imaging speed and, if exposed to extreme light, can eventually harm the samples.
With the SHy-Cam, the scientists had the ability to utilize the brand-new algorithm to acquire spectral info rapidly and effectively, in a video camera that can be developed with currently readily available optical parts. The brand-new devices explained in the paper can obtaining 30 information sets per 2nd, with a photon effectiveness of over 80%. This makes it an effective tool for multi-color, in-vivo imaging, the scientists stated.
“How do you produce a two-dimensional photo with a 2D sensing unit? You take a photo,” Cutrale stated. “Our difficulty is how to record a 3D information set with a 2D sensing unit. A normal color sensing unit gets 3 colors– red, blue and green– or it gets whatever through its grayscale sensing units.
“In our case, we require to ask for 42 channels of info– that’s not typical, nor is it effective. We created in this paper a brand-new technique that can acquire an encoded variation of the spectral details with a single image.”
Cutrale stated they do this by using light. The group harnessed light to change the info and utilized it to carry out the estimations prior to compressing it on to the sensing unit. In utilizing this method, the group demonstrated how it can get the whole spectrum and the measurements of the image.
“We’ve caught the X- and Y-axes of the image– its height and width– and likewise the spectral info on the wavelength-axis, completely in a single image with a basic video camera,” he stated. “That’s rather an effective method. We got performances in this hardware technique which remain in some cases as much as 8 times faster than existing instrumentation. To put it simply, 8 times more light reaches the video camera sensing unit in this compressed style.”
More details:
Francesco Cutrale, a Single-shot Hyperspectral Phasor Camera for quick, multi-color fluorescence microscopy, Cell Reports Methods (2023 ). DOI: 10.1016/ j.crmeth.2023.100441. www.cell.com/cell-reports-meth … 2667-2375( 23 )00056-5
Hsiao Ju Chiang et al, HyU: Hybrid Unmixing for longitudinal in vivo imaging of low signal-to-noise fluorescence,Nature Methods(2023 ). DOI: 10.1038/ s41592-022-01751-5
Citation: Pictures inside a cell: Researchers establish brand-new tool to offer higher insight into biological procedures (2023, March 31) recovered 2 April 2023 from https://phys.org/news/2023-03-pictures-cell-tool-greater-insight.html
This file goes through copyright. Apart from any reasonable dealing for the function of personal research study or research study, no part might be replicated without the composed authorization. The material is attended to details functions just.

